Improving the Air Levels of Cities with These 10 Things
In our environment today, breathing fresh air seems to be impossible. The air quality that we have now is slowly becoming a threat to public health, especially in big cities. We encounter a lot of cars roaming around and spreading pollution, and most of these have contributed to the death of 6.1 million people worldwide every year.
There is hope because here are 10 things we can do to improve air levels and encourage others to take charge. Changing how you live can save millions of lives.
#1 Traffic organization reduces congestion
The heavy flow of traffic can produce a lot of pollution in cities especially if cars do not undergo emission testing regularly. City planners should understand how traffic flows, and the areas from which most people are coming and where they are going. Dense residential areas are where people come from to go to work and go to after work. The roads leading to and from these areas will be the most affected by traffic congestion.
In some areas it is really difficult to change the traffic movement through bottlenecks, but there are ways that this can be dealt with. Redirecting traffic through other areas, but also organizing streets so that traffic flows in separate lanes before a bottle neck will help reduce the amount of traffic stuck at a congestion zone. Also, using technology to inform drivers of traffic up ahead can limit traffic. Similar to Google Maps function to see traffic in the path ahead, apps like Waze allow the same location tracking of where devices (and therefore people) are slowing down and then suggests alternative routes for drivers that need to get to the area they’re going to.
You can encourage your city to come up with a traffic plan. For example, suggesting to lessen the number of cars traveling in specific areas during certain hours is a good way to reduce bottlenecks in traffic.
#2 Public Transport
Instead of taking your own car to work, you can take public transportation. You can help lessen air pollution in the city in your own little way. Public transport promotes less exhaust fumes and more environmentally friendly especially subways and or double-decker buses. When you think about having to wait for your ride all the time, you usually look for an alternative.
Nobody likes to wait. However, in a big city, owning a vehicle and paying for the costs of running and parking one should sway your mind to leave transportation to the city. A city has to try it’s best to add routes for

every residential area, with enough stops and enough rides per hour so that the waiting time for riders is reduced. Subways and undergrounds work efficiently as well, and because the prices are usually subsidized by the city, they become an affordable option for the majority of city residents.
#3 Parks and Trees
Recreational areas are a must for big cities. Not only do people enjoy watching their kids play, but people can also relax under the shade of a big tree. A cities livability rating is determined by how people rate their lives living in that place. Parks allow people to exercise, relax and get fresh air.

The greener in a city, the more people enjoy being outside and enjoying nature. Actually, nature has proven to increase concentration and has lots of other benefits. Plus, a common fact about trees is that they remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, leaving us cleaner air to breathe.
#4 Air Management in Construction Zones
As cities grow, construction is imminent. The laws in place to manage pollution from construction are very important because it keeps residents safe. Specks of dust and debris caused by the construction sites in the city can contribute to air, water, noise and PM2.5 pollution. It is recommended for construction sites to install barriers like nets and barriers in place to contain dust within a construction site. Here are some ways that construction sites can reduce their pollution.
Air
- Never burn waste materials
- Use new machinery or keep diggers, excavators and anything with an engine maintained
- Use low sulfur diesel
- Use particulate filters and catalyst converters
- Use water sprays and sprinklers to control the pollution
- Use ‘on-tool’ extraction that remove exhaust directly where they are produced
- Source local materials
- Use renewable and sustainable materials
- Wear appropriate Personal Protection Equipment
Water
- Monitor and improve disposal of waste
- Keep materials secure so that they don’t go into waterways
- Cover up all drains during construction
- Keep the road and footpath to the site clean at all times
- Properly collect and treat wastewater
Noise
- Use new and quiet tools
- Limit working hours to be sociable as not to disturb residents. Notify them!
- Put acoustic barriers in place
- Ensure equipment is maintained
- Switch off engines when not in use
Source
#5 Industrial Production Limiting
Several power plants within the city can harm people’s health and therefore, should be limited. If not, they should be asked to transfer to locations that are away from the public. These days it is easy to produce electricity with the power of the sun, water or wind. Coal power plants and other high polluting plants should be limited.
#6 Law on vehicles and fuel standards
Coding schemes should be modified to affect a city’s vehicles. his will lessen the volume of vehicles hourly, but also decrease the amount of pollution. Fuel standards are put in place so that vehicles emit less pollution. The age of engines and how they are  maintained is monitored in many cities. Emissions stickers are only given to vehicles in America if the engine passes a yearly test. Many countries are lacking mandatory vehicle testing so this is really important for developing countries. Many developing countries also are not yet adhering to the best fuel standards. This means that there are more pollution emitting particles in the exhaust fumes.
maintained is monitored in many cities. Emissions stickers are only given to vehicles in America if the engine passes a yearly test. Many countries are lacking mandatory vehicle testing so this is really important for developing countries. Many developing countries also are not yet adhering to the best fuel standards. This means that there are more pollution emitting particles in the exhaust fumes.
#7 Large vehicle inspections
Large vehicles are the biggest contributors to black carbon that can be harmful to the public once inhaled. Minimized travel periods of these vehicles and emission testing certificates issued to these vehicles will definitely reduce pollution. Often large vehicles like excavators, tractors or trucks have larger engines which produce more exhausts. For more information on different vehicles and their pollution, see this article [link].
#8 Subsidize Green Energy
A renewable energy source is essential to reducing air pollution. Not having to depend on our fossil fuel energy sources is the way forward. Many countries are now jumping on the clean energy train, setting up solar panels, windmills and building more dams. Unfortunately, there are still plenty of countries running completely on nuclear and coal powered energy plants.
Let’s take a look at Iceland. 87% of it’s energy comes from hydro-power and the other 13% comes from geothermal power. Now Iceland is a small country with a small population but other countries can quickly catch up if they start investing in green energy
Take a look at the Netherlands, with thousands of windmills in the country and off the coast. The government has set up a subsidy for production of renewable energy in 6 different categories: biomass, geothermal, water, wind and sun. As follows, a wonderful example of how individuals can invest in green energy and even make money back from it in the future. They have made it super easy for any resident of The Netherlands to buy a part of a windmill. Once their investment has paid off, they can either use the energy their share produces in their own homes, or they can sell the energy they make.
#9 Trash Collection
Collecting trash should be done on a daily basis. Large numbers of residents who produce more than 1 kilo of trash each per day create a lot of trash. As someone who cares about the environment, you might recycle your trash. Recycling can lessen the amount of pollution caused by biodegradable garbage mixing with other types. The main thing a city can do to reduce trash fires is to collect trash at set times. If there aren’t enough collection trips per area, the trash is left behind.
Large numbers of residents who produce more than 1 kilo of trash each per day create a lot of trash. As someone who cares about the environment, you might recycle your trash. Recycling can lessen the amount of pollution caused by biodegradable garbage mixing with other types. The main thing a city can do to reduce trash fires is to collect trash at set times. If there aren’t enough collection trips per area, the trash is left behind.
n many places the trash is trouble for the residents so they decide to burn it. This is exactly what we don’t want to happen. Collecting trash and bringing it to a sorting center before it goes to a trash dump is  necessary for any country to organize. Hiring private companies that can make money and pay salaries well is key to making sure everything is getting picked up. Additionally, keeping all of the collector’s equipment and vehicles should be maintained to be able keep the correct quota of trash pickups efficient and effective.
necessary for any country to organize. Hiring private companies that can make money and pay salaries well is key to making sure everything is getting picked up. Additionally, keeping all of the collector’s equipment and vehicles should be maintained to be able keep the correct quota of trash pickups efficient and effective.
#10 Ban burning
Waste has chemicals that can pollute the air and suffocates people when burned. Take into account the banning of burning garbage within the city. There are different reasons why people burn things, but the biggest is a lack of education. People don’t have the luck of being brought up in a household that can afford a proper education for their children. When they grow up, they continue their bad habits like disposing of trash on the street and even burning it to get rid of it.
Some places simply have far too much trash, so they get tired of smelling the vile scent of choking. Sometimes it’s the only solution. That is where laws come in, and together with organized trash collection, burning can be stopped.
The burning of stubble to quickly prepare for a new crop season is another reason smoke fills city surroundings. These tactics of burning to increase the quality of soil can easily be changed by using the material that is normally burnt could be tilled. It can effectively be mixed back into the soil to reap the same rewards. Simply understanding the science behind how burning can affect us and educating those that don’t yet know is probably the best and only way forward to start making changes.
Conclusion
Start the change within yourself by encouraging and influencing others to do the same things as well. Help your city become less polluted for the better good of the community and for our future generations to enjoy. With these 10 tips for city standards and adjustments, our lives can improve. It will take hard work, a lot of planning, and policies for us to live in a paradise with no pollution, but we have to start somewhere!







 nts to our forecasts.”
nts to our forecasts.”










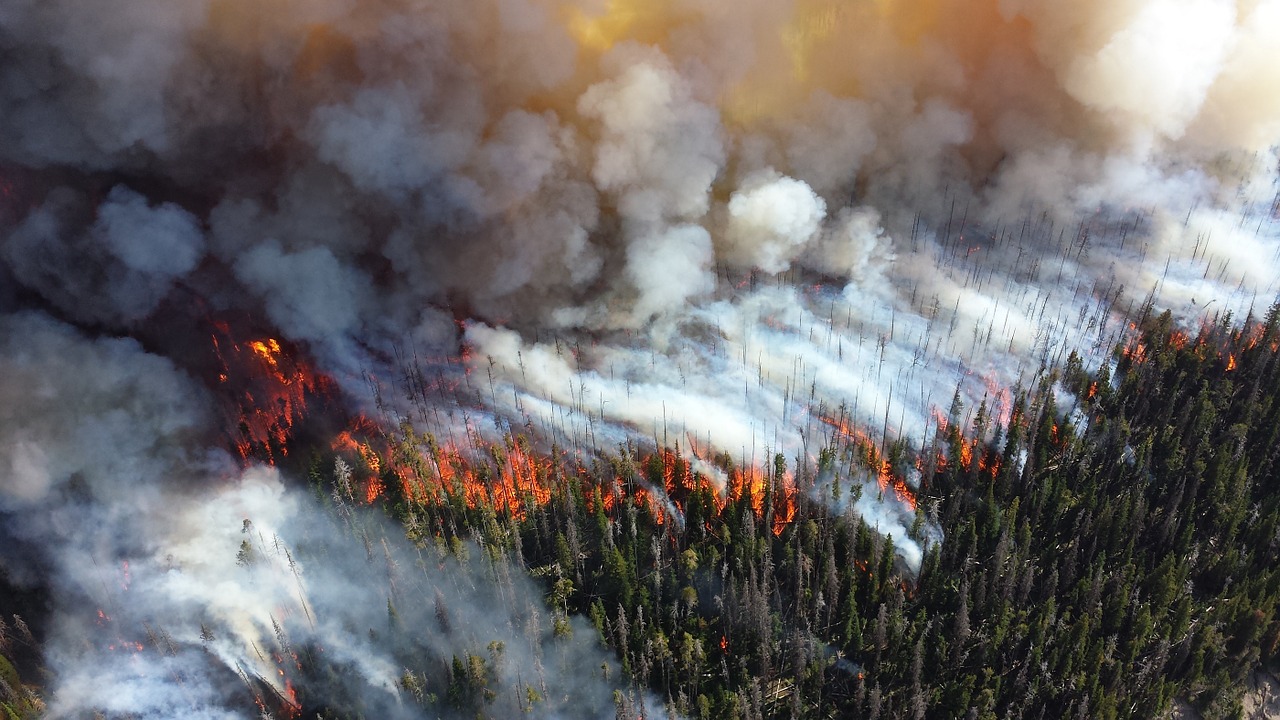
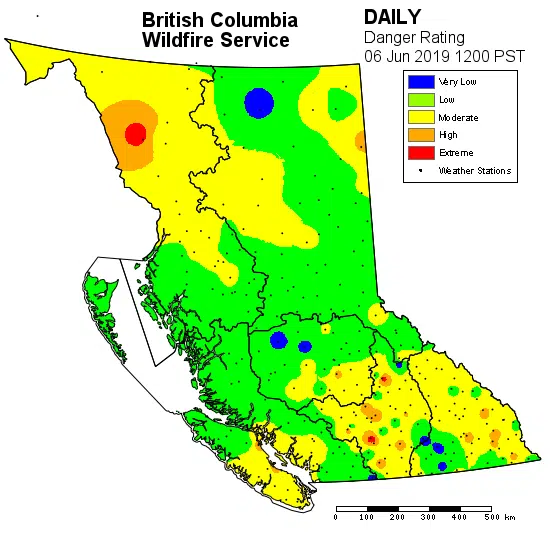 The zone usually depends on dryness, but that qualifies where the fires may start. Once a fire has started, the pollution depends on the wind speed and direction. Look at 1 example of
The zone usually depends on dryness, but that qualifies where the fires may start. Once a fire has started, the pollution depends on the wind speed and direction. Look at 1 example of